DISEASES
When the rhythm of the heart is not normal, then we say that arrhythmias occur.
The most common conditions are syncope, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, tachycardia, and other less common ones.
SYNCOPE or UNEXPLAINED FAINTING
The sudden loss of consciousness — also called "fainting" or syncope, which occurs when blood pressure drops, and oxygen cannot reach the brain. Why is tracking needed? Fainting can be severe when caused by an irregular heart rhythm.
PALPITATIONS
A typically harmless state in which we feel our heart pounding, running fast or fluttering. Why do I need monitoring? Palpitations may indicate a serious underlying heart condition.
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
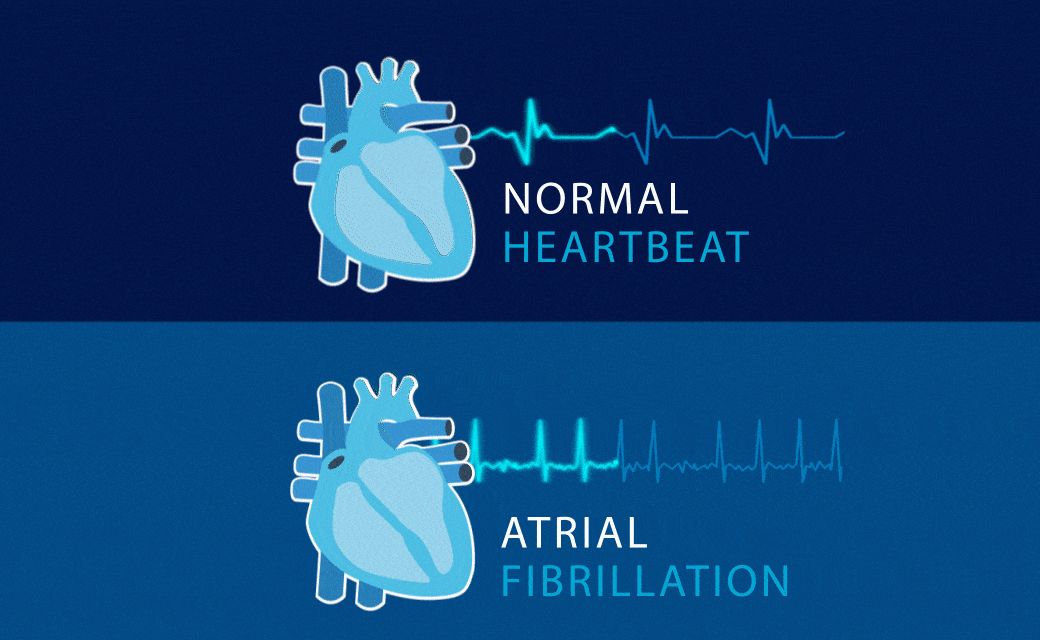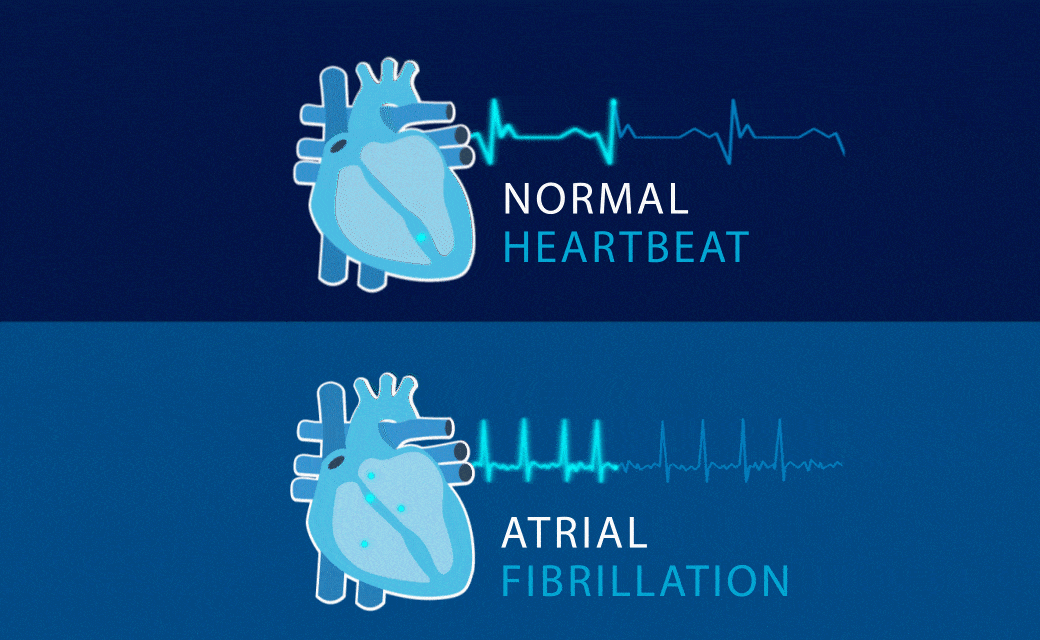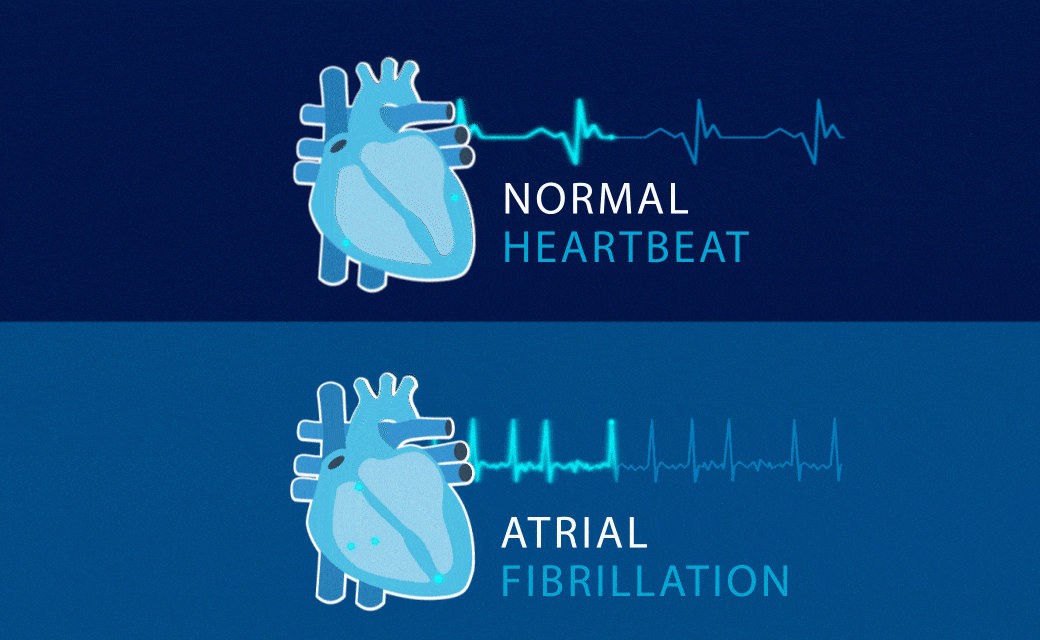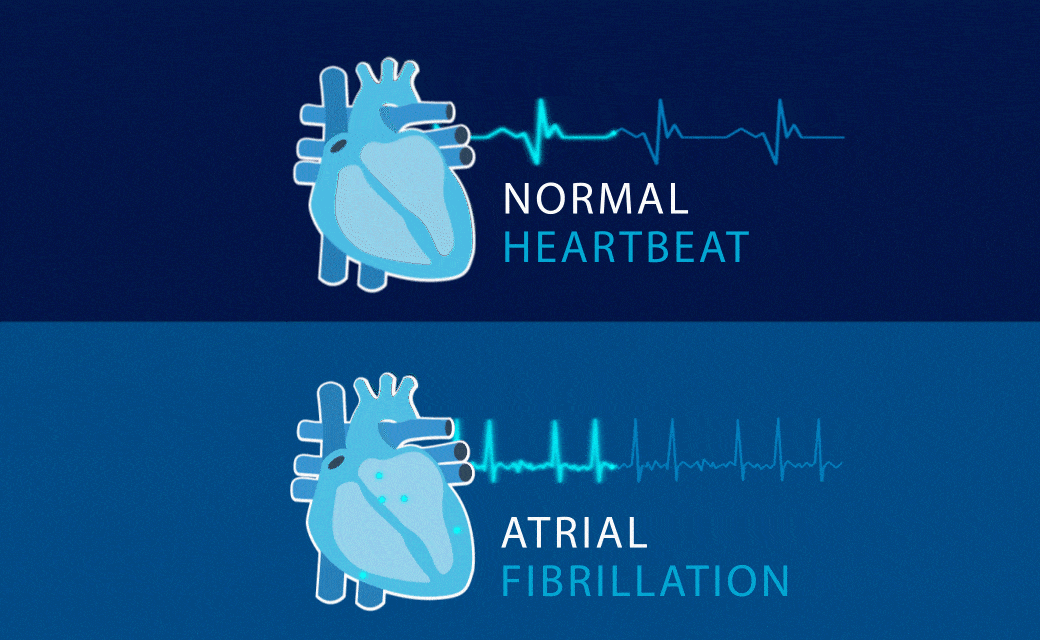
Common condition in which the upper chambers of the heartbeat too fast and irregularly.
Also called AF. Why is tracking needed? AF requires treatment because it is closely related to stroke.
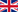
WHAT IS BRADYCARDIA?
Bradycardia is a condition in which the heart beats too slowly. A healthy heart beats 60 to 100 times per minute, pumping about 280 liters of blood every hour. With bradycardia, the heart beats fewer than 60 times per minute. At that rate, the heart is not able to pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the body during normal activity or exercise.
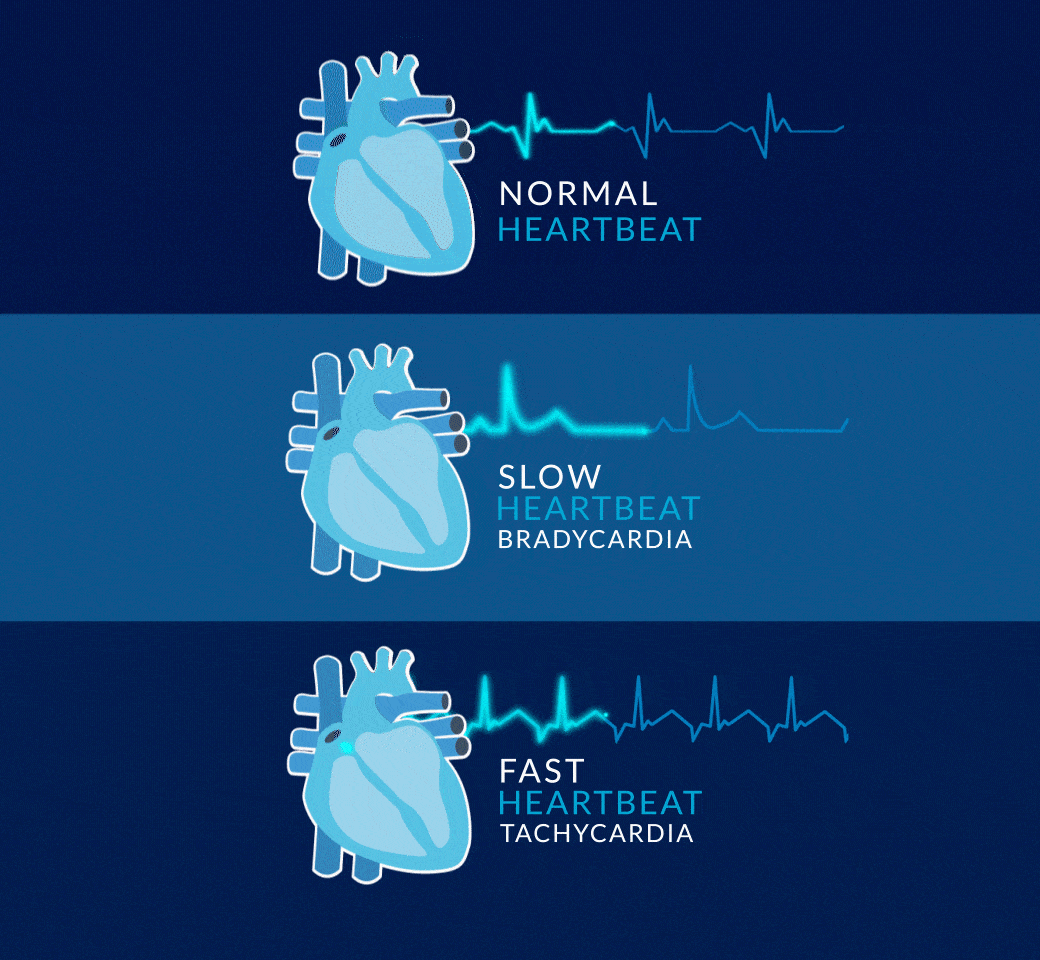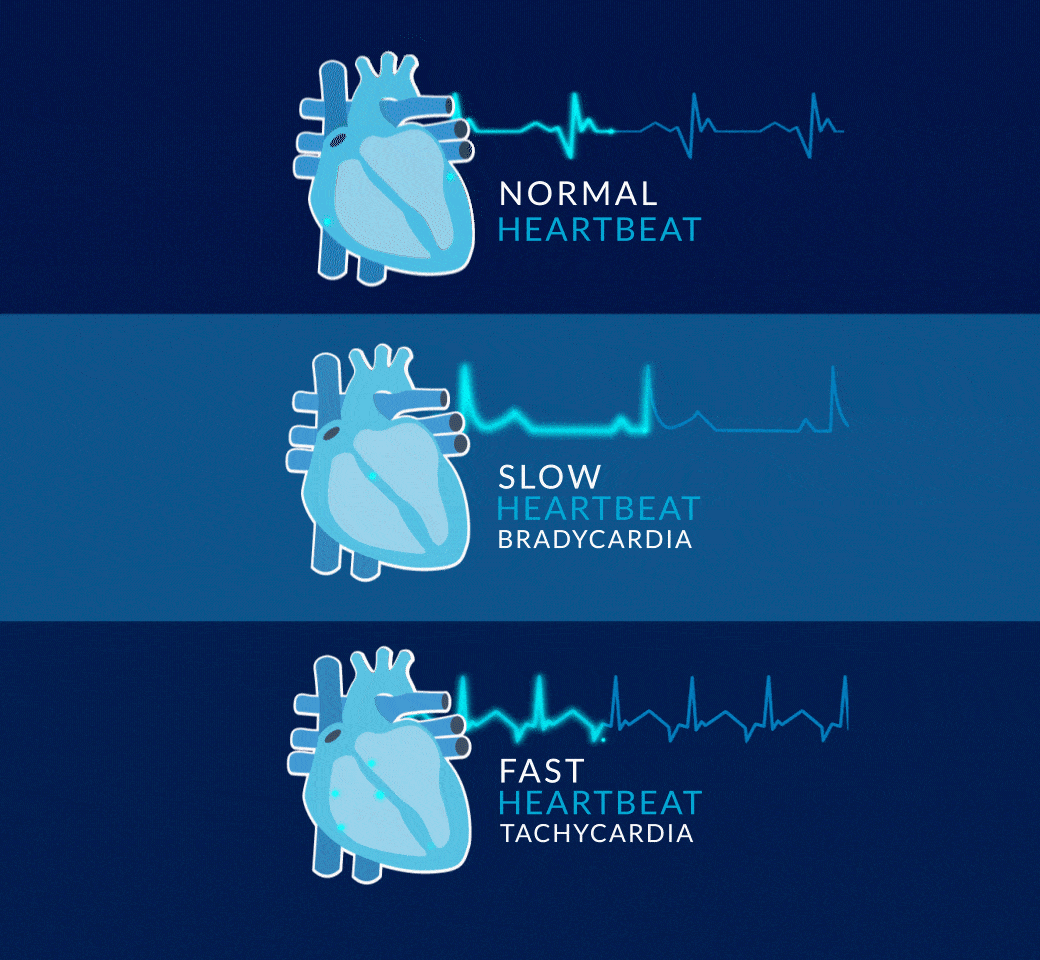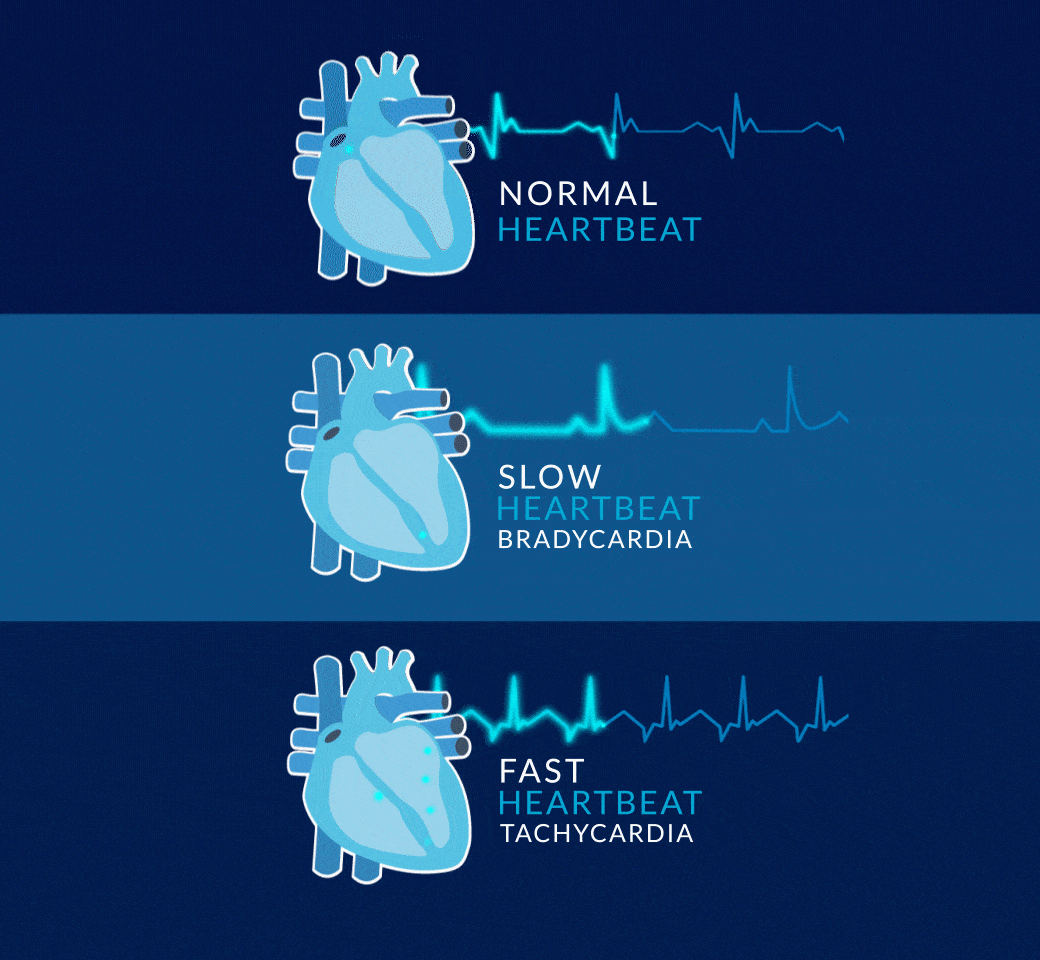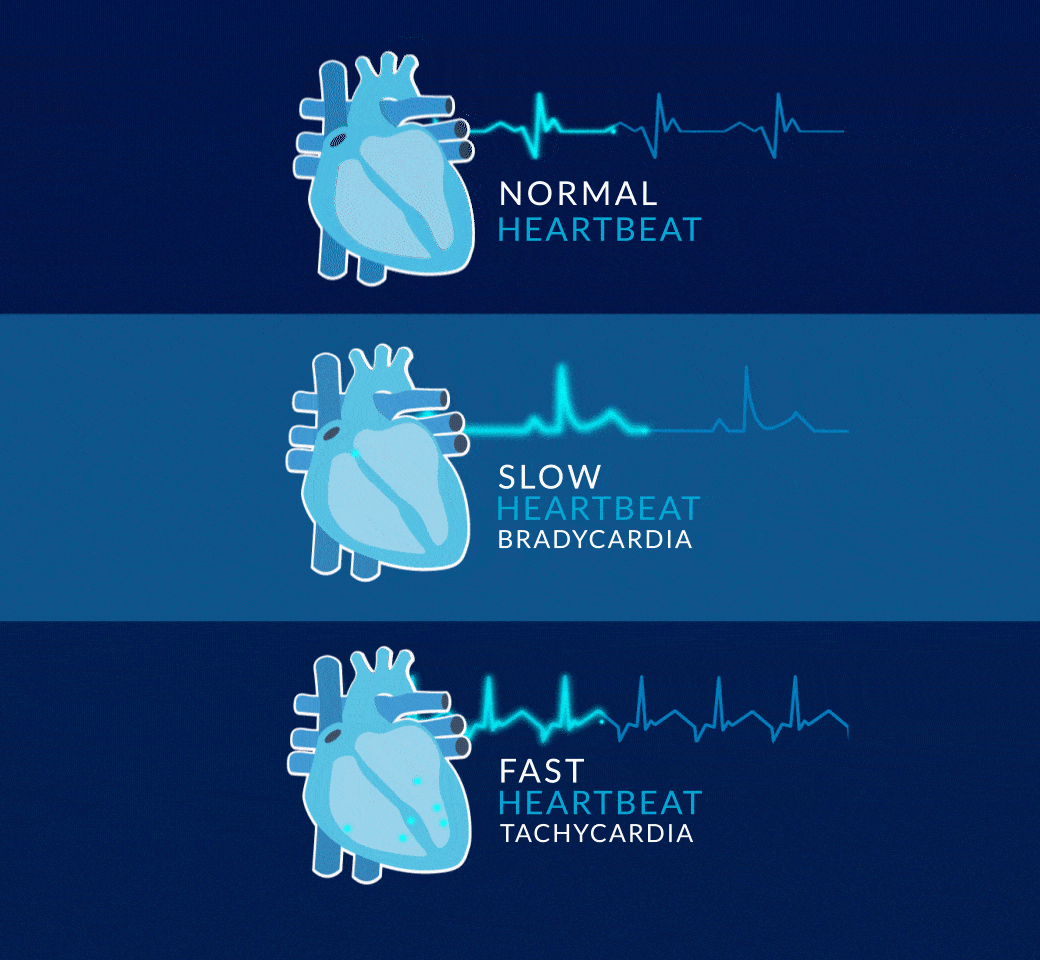
WHAT IS TACHYCARDIA?
Tachycardia is a condition where the heart beats too fast. A healthy heart beats 60 to 100 times per minute, pumping about 280 liters of blood every hour. Exercise, stress or fear can cause the heart to beat faster, but this is a normal response. With tachycardia, the heart beats at more than 100 beats per minute and can beat as fast as 400 beats per minute for no specific reason. At this rate the heart is not able to pump blood effectively to the body and brain.
There are different types of fast heart rhythms that can occur in either the upper chambers (atria) or lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart:
-
Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation start in the upper chambers of the heart
-
Ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation start in the lower chambers of the heart
Learn more about Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias
WHAT IS HEART FAILURE?
The term heart failure does not mean your heart has stopped pumping; rather, your heart muscle is not able to pump enough blood to meet your body’s needs. As a result, you may feel tired, lack energy, experience shortness of breath and notice excess fluid collecting in your body.
ΜLearn more about Heart Failure
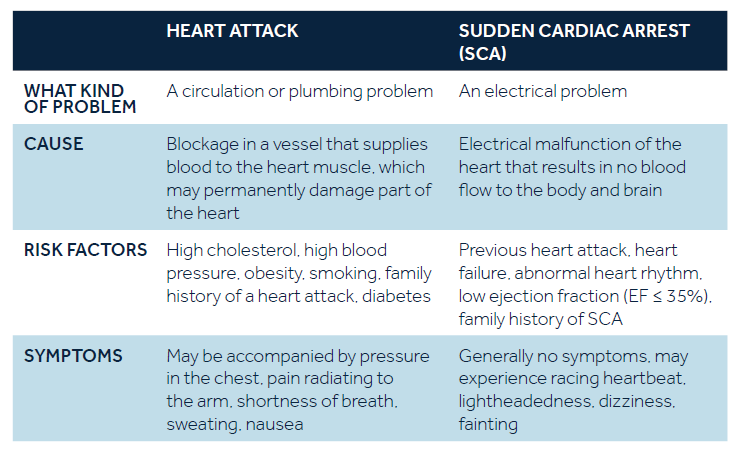
WHAT IS SUDDEN CARDIAC ARREST?
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) results from an electrical problem with the heart that triggers a dangerously fast heart rhythm (ventricular fibrillation). The rapid, irregular heart rhythm causes the heart to quiver rather than contract or pump. When the heart stops pumping blood, oxygen cannot reach the body and brain. If not treated immediately, SCA can be fatal. Sudden cardiac arrest is one of the top killers and claims more lives than breast cancer, AIDS, or lung cancer.
Learn more about Sudden Cardiac Arrest
HEART ATTACK AND SCA: WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES?
Sudden cardiac arrest is not the same as a heart attack, although the two are often confused.